Introduction
Anatomy is the study of human anatomy. This discipline examines all parts and organs within our bodies including our bones (bones), muscles (muscles) nerves (nerves) as well as circulation processes such as blood flow.
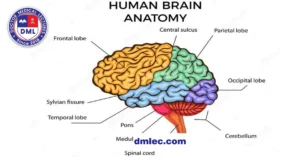
Anatomy can be divided into two major branches. Gross involves studying organ structures visible to an untrained observer, including bones, muscles, and the cardiovascular system. Microanatomy This field specializes in areas that can only be studied under a microscope, including tissue and cells.
Anatomy Understanding the Human Body
Anatomy refers to the study of human anatomy. Body. It offers vital insights into how our body’s structure functions across all areas, from the smallest cells to the complex systems that allow life. Analyzing anatomy helps us understand how organs interact with tissues and the structures that will enable us to function. This area will allow us to connect biology and medicine, essential to understanding the human body’s health and ailments.
The Importance of Anatomy
Anatomy is a crucial aspect of medical sciences. It’s an essential element of health and education. The importance of can be attributed to its capacity to:
- Aid Medical Professionals Medical professionals heavily rely on anatomical knowledge to diagnose and treat ailments quickly. Knowing the body’s helps surgeons perform precise surgery, and physicians develop precise treatment programmes.
- It forms the foundation for studying at advanced levels to help educate students in medicine nur, nursing, and other related health sciences. It is the basis of anatomy and pathology and many different disciplines.
- Research Help Analytical research has led to revolutionary advances in the healthcare field, including developing novel surgical techniques and investigating the mechanisms behind diseases.
- Enhance everyday Knowledge Beyond the medical applications; Anatomies aid people in understanding how their bodies work to provide better medical treatment and enhanced consciousness.
Key Components
Human bodies are constructed by multiple layers of organization structure, which are more complex than the previous one. They are:
- Cells:
- The foundation of life.
- They have specific functions essential to cell survival, which include the generation of energy, the elimination of waste, and the replication of cells.
- The specific cells are red blood cells, epithelial neurons, and neurons.
- Tissues:
- Cells that have a similarity to one another and that are working on a particular project.
- The four most common kinds of tissues:
- Epithelial Tissue: It protects and covers the zones.
- Connective Tissue Organization and Support.
- Muscle Tissue helps to move.
- The nerve tissue sends out signals that allow message transmission.
- Systems:
- Organs are organized into structures that perform vital functions to sustain living.
- Principal systems comprise:
- Skeletal System offers structural assistance.
- Muscular System: Enables movement.
- The nervous system is a system that processes and transmits data.
- Cardiovascular System circulates blood.
- Digestive System: Processes nutrients.
- Respiratory System: Facilitates gas exchange.
- Endocrine System: Regulates hormones.
- Immune System: The system protects you from the spread of disease.
Branches of Anatomy
Gross
-
- It is focused on large visible structures like bones, muscles and organs.
- Examined through dissection and imaging methods such as radiographs and MRI.
- Microscopic:
- Examines structures that can’t be observed by the naked eye, like tissue and cells.
- This is a study of the cytology (study of various cell types) and Histology (study of tissues).
- Developmental:
- Explores the changes in the body’s structure during pregnancy and into adulthood.
- It also includes embryology, which focuses on the prenatal stage of development.
- Comparative:
- Human anatomy can be studied about of different species to understand better how evolution has occurred and what adaptations occur.
- Clinical:
- Use anatomical Knowledge in clinical settings, helping in the identification and treatment.
Applications of Anatomy
Anatomy covers a wide range of applications that can be found across various fields:
- Medicine and Surgery:
- Understanding is vital to formulating successful surgical procedures and medical treatments. For instance, knowing how the heart functions is essential during heart surgery.
- Sports Science:
- Athletes and professional athletes use anatomical info to enhance the performance of athletes, improve their training techniques, and avoid injuries.
- Forensic Science:
- Specialists in Forensics utilize to find human remains, as well as discover the causes of death when conducting legal investigations.
- Biomedical Research:
- Analytical studies help in the design of devices for diagnosing and assessing prosthetics as well as the creation of delivery methods for drugs.
- Education and Public Awareness:
- courses are taught at the university level in schools, universities, and various public health programs to raise awareness about the human body and promote well-being and health.
A few of the most powerful instruments and methods include:
Cadaveric Dissection:
A traditional technique is where students and professionals study the human body’s parts to gain Knowledge.
Modeling and Virtual Reality (VR).
- It is a chance to engage and participate in examining. Students can imagine the structure of three dimensions.
Wearable Technology.
Instruments that measure crucial parameters like the heart rate and muscle activity link with live data.
Digital Apps and Software.
Educational applications like Visible Body, as well as medical, offer-related information for students all over the world.
Challenges in Learning Anatomy
Anatomy is fascinating to study. However, it has its problems of
- Volume of Information:
- Human body systems are extraordinarily complicated and require multiple structures and words to be recalled.
- Retention and Application:
- Many students struggle to keep track of and apply their Knowledge of to actual situations.
- Technological Barriers:
- Access to cutting-edge technologies like VR may be restricted to specific locations or establishments.
Tips for Mastering Anatomy
- Break It Down:
- Focus on one particular region or system for a moment so you don’t feel overwhelmed.
- Use Visual Aids:
- Models, diagrams, and video clips are fantastic methods of making complex concepts easier to understand.
- Engage in Hands-On Learning:
- Engage in dissections or make use of 3D tools for learning interactively.
- Practice Regularly:
- It’s crucial to be aware of your Knowledge. Examine notes and take tests regularly.
- Connect Concepts:
- Integrate anatomical Knowledge with actual clinical scenarios or real-world situations to improve Knowledge.
Conclusion
The extends beyond studying organs and components. It’s an approach to understanding the complex mechanism that drives the living. From medical procedures to everyday understanding of the human body, is an integral component of life for humans.
1.What is Anatomy?
The study of body structure including organs, tissues, systems and cells in relation to one another.
2.Which are the primary kinds of anatomy?
Anatomy can typically be divided into two classes.Gross Anatomy (or) refers to the study of body parts visible to naked eyes; Microscopic focuses more closely on structures like tissues and cells which require inspection through microscope.
3.What Is the Importance of Anatomy?
Anatomy provides insight into human physiology and function. Understanding provides essential understanding when diagnosing and treating illness; additionally it forms a cornerstone subject matter for healthcare providers as a basis of education and practice.
4.Who studies anatomy?
Anatomy is studied at medical schools, health specialists, physiotherapists and nurses as well as by other workers working within biological or medical sciences fields.
5.What systems will I learn in anatomy class?
Our anatomy course explores many body systems including.Skeletal System, Muscular System and Nervous System. Circulatory system are components that form part of an organ’s functionality; respectively.
